VACCINEGATECORVELVA STAFF MARCH 31, 2020

We are finally here, after almost two years the first peer review publication of our analyzes comes out and many others will follow.
Here we try to summarize in these first pages, in a very discursive and non-technical way: what has been published, what validity it has and why it is important for our investigation of vaccines.
(The following pages to 3 are instead dedicated to a technical in-depth analysis, finally leaving the evaluation of the article itself to the experts in the sector)
What was published in “F1000 Research” 1 is the result of the initial part of the work carried out on behalf of the Corvelva Association by one of the laboratories in charge of the analyzes. We remember – because more than two years have passed since the beginning of this work and many other results have been added to the initial ones – that the first major issue that we found ourselves having to investigate was the abnormal quantity of human DNA found inside of the vaccines analyzed.
In both quadrivalent MPRV vaccines analyzed, quantities of 1 to 2.7 micrograms / vial were initially found (as per publication in question), and this led us to publicly and immediately denounce this result because, simply, it was not expected that a this amount of DNA was present in a vaccine.
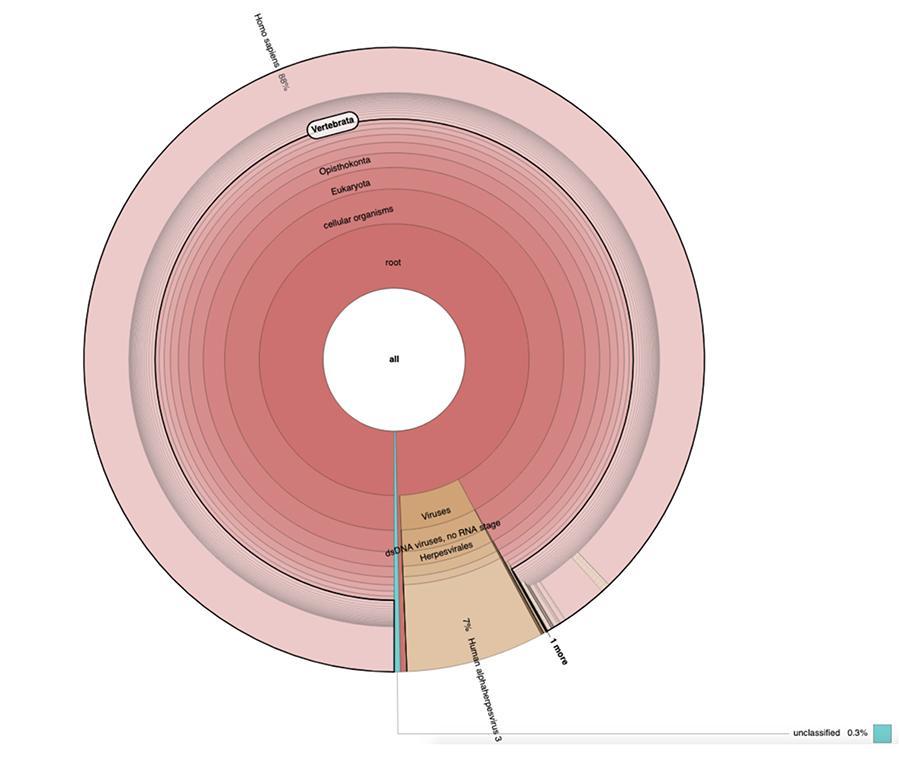
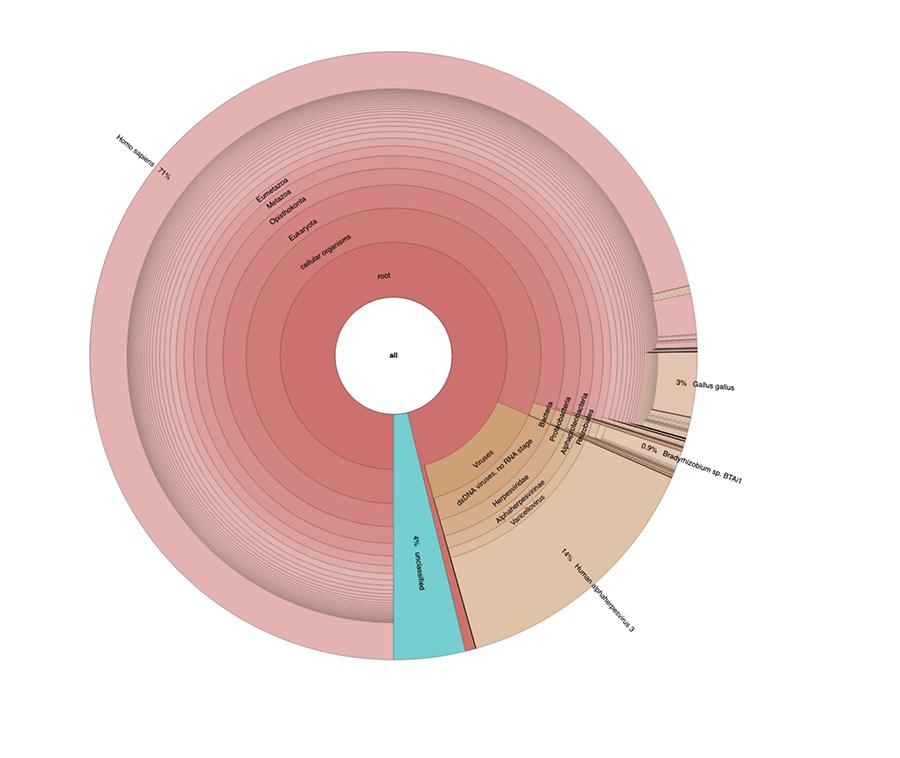
Apart from the considerations and conclusions reached by the work, which are strictly technical and therefore understandable only to those who research in the field of metagenomics, what is observed in the graphs is that the two vaccine samples were found to contain a high percentage of readings of human DNA in addition to those expected of the genome of the varicella virus (Human alphaherpes virus 3), the only one detectable among the four, having been presented in the article a DNA-seq type analysis.
However, we would like to underline that subsequently the quantities of DNA found and confirmed with the same method that is now validated here were even higher: up to 3.7 micrograms per vial, leading to a notable difference between lot and lot.
In fact, in our report released on 22.12.2018 2 the results for further batches analyzed after those discussed in the article were reported , then further confirmed by interlaboratory analyzes which are still being published.
Therefore, what most interests us about this publication is that it validates the method used , puts an important point on the discussions on the “type” of analyzes carried out, and consequently confirms decisively all the work carried out subsequently with the NGS method. : the in-depth analysis on the type of genetic material contained, the presence of adventitious viruses, the great absence of attenuated viruses that should instead exist and the quantity instead out of control (also because very different from sample to sample) of the human DNA present, the mutant population , phages, DNA deriving from other species, and gradually all the results that you find summarized on our site. 3
Everything that, from the point of view of biological content, we have denounced in recent years, slavishly reporting the results to the control bodies, takes on a more relevant scientific connotation (even if, we repeat again, it was not peer-reviews that had to worry but the data presented, very serious in their content and in their possible implications for human health). However, now that the publication of the method has been done, we will demand to obtain the answers that have not yet arrived.
These results unquestionably confirm the presence of fetal DNA in Priorix tetra vaccines, in variable quantities between the various batches, indicating a poor quality control of these pharmaceutical products.
We also recall the report on the sequencing of the entire genome of MRC-5 published on the Corvelva website on 27.09.2019 4 in which the profound modification of this DNA is evident also in genes associated with the development of tumor pathologies (another data in progress publication).
The contaminating fetal DNA present in all samples analyzed in variable (therefore uncontrolled) quantities is up to 300 times higher than the limit imposed by the EMA for carcinogenic DNA (10 ng / dose, corresponding to the DNA contained in about 1000 cancer cells, obtained on the basis of a statistical calculation, while the precautionary limit is 100 pg / dose) limit that must necessarily also be applied to the fetal DNA that inevitably contaminates the Priorix Tetra.
It follows that this vaccine must be considered defective and potentially dangerous for human health, in particular of the pediatric population much more vulnerable to genetic and autoimmune damage due to immaturity in shelter systems.
As anticipated, the following is a more “technical” part and difficult to understand for non-experts, therefore we have decided, also for transparency, to attach to this document also the “Dossier EMA – NGS Discussion of the results obtained from the survey on the quality of vaccines “ . We had to extrapolate only the disclosable part, over 50 pages of the dossier compared to the 200 of the NGS, since much of the information contained and registered with the regulatory bodies must remain confidential. The harsh law of science provides that a data can be published in a journal only if unpublished and we, having several other publications in the works, do not want to put them at risk.
Finally, for the avoidance of doubt, we would like to mention, from the publication, the part of the “Funding Statement”:
“B1 and B2 metagenomic sequencing was funded by Corvelva (non-profit association, Veneto, Italy), under a service contract with the laboratory. No other contributions were involved in supporting the work. Funders played no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or manuscript preparation. “
Attachments:
- Publication – Do you cov me? Effect of coverage reduction on metagenome shotgun sequencing studies
- CORVELVA-discussion-NGS-EMA-eng
- PDF – First peer review publication on MPRV vaccines (Priorix Tetra)
In the article “Do you cov me? Effect of coverage reduction on metagenome shotgun sequencing studies “
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7059852/
The authors address the technical-methodological question of whether it is possible to use a parallel massive metagenomics approach with low reading coverage to characterize complex biological matrices. Estimates of diversity and abundance of species are calculated and the ability to reconstruct the metagenome de novo in terms of length and completeness is evaluated, in order to understand how much the decrease in sequencing depth, varied by randomly sub-sampling the sequencing readings, can The results show that the diversity indices of prokaryotic, eukaryotic and viral complex communities can be accurately estimated with 500,000 reads or less, although particularly complex samples may require 1,000,000 reads. In reverse,
Among the various, and very different, complex matrices subjected to massive metagenomic analysis, two biological medicines were included, i.e. two different batches of live attenuated MPRV vaccine used for immunization against measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox in children. DNA was extracted from the vaccines, genomic libraries were then built using standard commercial protocols and massive sequencing was carried out with Illumina technology.
Apart from the considerations and conclusions reached by the work, which are strictly technical and therefore understandable only to those who research in the field of metagenomics, what is observed in the pie charts contained in the ‘Extended data’ (https://osf.io/wq395/ samples B1 and B2) is that the two vaccine samples were found to contain a high percentage of human DNA readings in addition to those expected from the genome of the varicella virus (Human alphaherpes virus 3), the only detectable among the four, since a DNA-seq type analysis was presented in the article.
71% of the readings in one lot and 88% in the other are of human origin, presumably from the MRC-5 fetal cell line ( remember that subsequent analyzes confirmed that the line is MRC5 ) in which live attenuated rubella and chickenpox viruses are grown during vaccine preparation. Furthermore, as happened in the different batches of the same MPRV vaccine tested by Corvelva between 2017 and 2019, the amount of DNA extracted is of the order of a microgram.
In vaccine batches tested with the same protocols and technology reported in the materials and methods of the article, the quantities detected ranged between 1 and almost 3 micrograms per vial, quantities varying from one batch to another, but always significant.
In the report disclosed by Corvelva on 22.12.2018, the following results were reported for further batches analyzed after those discussed in the article , then further confirmed by interlaboratory analysis still being published:
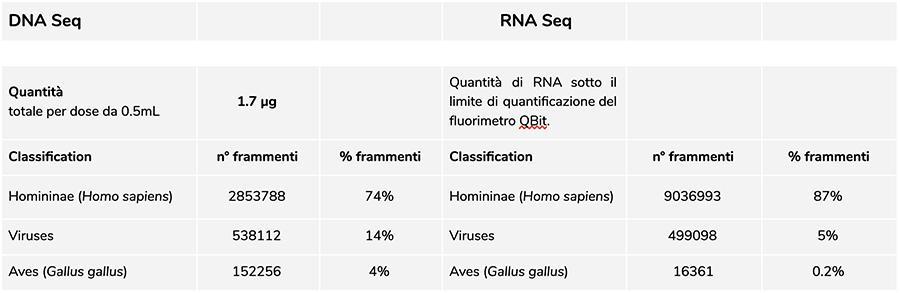
Priorix Tetra lot. A71CB205A (June 2018) – DNA analysis
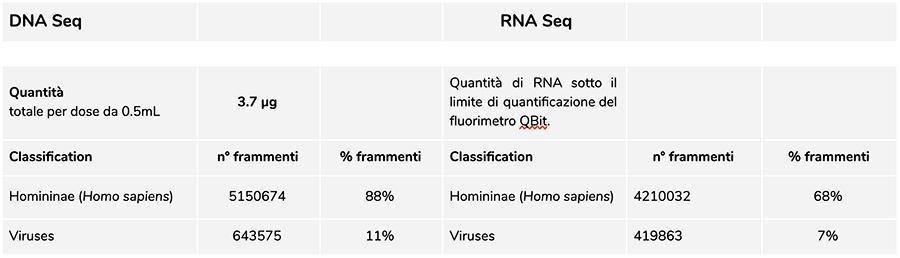
Priorix Tetra lot. A71CB256A (December 2018) – DNA analysis
DNA analysis
The measurement of the DNA concentration with QuBit fluorometer showed that lot A71CB205A, contains a quantity of gDNA of 1.7 µg total per 0.5mL dose, calculated as follows: 9.41ng / µl (concentration determined at QuBit) x 45 (volume of resuspension DNA final after extraction, expressed in microliters) x 4 (the starting volume subjected to the extraction procedure is ¼ of the volume of the dose contained in the entire vial equal to 0.5mL).
The measurement of the DNA concentration with QuBit fluorometer showed that lot A71CB256A, contains a quantity of gDNA of 3.7 µg total per 0.5mL dose , calculated as follows: 40.8 ng / µl (concentration determined at QuBit) x 55 (volume of resuspension final DNA after extraction expressed in microliters) x 5/3 (the starting volume subjected to the extraction procedure was 300 µl on 500 µl of suspension).
The human DNA found in this lot is approximately 8 to 1 relative to chickenpox DNA (see results below of the DNA fragment classification-seq, which shows that 88% of the total sequenced DNA fragments are human origin, and 11% are from the varicella virus genome). Considering that NGS is a quantitative technology, the fluorimetric quantification of the total DNA extracted from the vaccine (e.g. lot. A71CB256A = 3.7 micrograms per dose), associated with the relative quantification consideration made above (8: 1), allows us to say that human DNA could be about 2.9 micrograms per dose , compared to about 740 nanograms of chickenpox DNA. It is also plausible thatat least a portion of the high molecular weight DNA that is seen on the gel may be high molecular weight human DNA.
RNA analysis
The quantity of RNA contained in the vial of vaccine lot A71CB256A was found to be about 200ng .
The RIN equal to 8 indicates an excellent quality RNA and an intact eukaryotic RNA, being present both the 18S and 28S peaks typical of eukaryotic RNA.
The answers to our questions forwarded to the regulatory agencies over time are of great importance. Currently, the agencies have not yet answered the questions regarding the results of the full analyzes delivered to the EMA and AIFA.
Extract from the EMA’s answer to our question about the safety of mrc-5 residues in the priorix tetra vaccine (EMA request reference ask-43967 3 august 2018) – “Based on published information, Priorix Tetra contains viral strains produced separately in chicken embryo cells (mumps and measles) or human MRC-5 diploid cells (rubella and chicken pox). The cell lines used for Priorix Tetra include human diploid cell lines that cannot divide continuously. Note that, according to the European Pharmacopoeia, MRC-5 diploid cell lines are not tumorigenic, as demonstrated by decades of use and control, and therefore an upper limit for MRC-5 cell DNA does not apply “
To date we have not been provided with evidence (neither in terms of product quality analysis certificates, nor scientific reference literature for the EMA) of these controls ensuring that it is appropriate not to apply an upper limit.
In the FDA guideline “Guidance for Industry: Characterization and Qualification of Cell Substrates and Other Biological Materials Used in the Production of Viral Vaccines for Infectious Disease Indications” 6 it is reported that:
- a diploid cell strain should always remain diploid. If these characteristics are not stable, it must be demonstrated that the instability does not adversely affect the production or conformity of the product.
- for widely used human diploid cell strains, such as MRC-5 and WI-38 cells, measurement of residual DNA may not be necessary because we do not consider residual DNA from these human diploid cells to be a safety concern
- residual DNA for non-tumorigenic continuous cells, such as low pass VERO cells, should be limited to less than 10 ng / dose for parenteral inoculation as recommended by WHO
And in the WHO guideline “Annex 3 – Recommendations for the evaluation of animal cell cultures as substrates for the manufacture of biological medicines and for the characterization of cell banks. Replacement of Annex 1 of the WHO technical report series, No. 878 ” 7 is added: (…) considerable experience has been accumulated on the cytogenetics of WI-38 and MRC-5 since the 1960s
and in support of this experience, the following articles are listed:
- Jacobs JP. Updated results on the karyology of the WI-38, MRC-5 and MRC-9 cell strains. Developments in Biological Standardization, 1976, 37: 155–156.
- Jacobs JP. et al. Guidelines for the acceptability, management and testing of serially propagated human diploid cells for the production of live virus vaccines for use in man. Journal of Biological Standardization, 1981, 9: 331–342.
- Petricciani JC et al. Karyology standards for rhesus diploid cell line DBS-FRhL-2. Journal of Biological Standardization, 1976, 4: 43–49.
- Schollmayer and et al. High resolution analysis and differential condensation in RBA-banded human chromosomes. Human Genetics, 1981, 59: 187–193.
- Rønne M. Chromosome preparation and high resolution banding techniques: a review. Journal of Dairy Science, 1989, 72: 1363–1377.
It can be clearly observed that the reference literature, to argue that the diploid cells used for the production of vaccines are safe from the point of view of genetic stability, is obsolete . The first genetic anomalies were already found 40 years ago, considered negligible for the safety of vaccines, and from what is reported in the WHO guideline, since then no updates have been made with new sequencing technologies, in particular in NGS, which is also economical. and rapid, with the consequence that in the vaccines administeredfor decades the presence of DNA progressively more and more genetically modified and in uncontrolled quantities has been allowed by agencies. In this regard, see the report on the sequencing of the entire genome of MRC-5 published on the Corvelva website on 27.09.2019 8 in which the profound modification of this DNA is evident also in genes associated with the development of tumor pathologies. (data being published)
Below is an extract from the letter from Dr. T. Deisher, a world expert in the therapeutic use of stem cells and gene therapy, which underlines the concern of the risks associated with the use of vaccines contaminated with residues. of human fetal cells:
Dr. T. DEISHER (letter to the rulers – April 8, 2019) 9 – (…) injecting our children with human fetal DNA contamination carries the risk of causing two well-established pathologies:
- insertional mutagenesis: human fetal DNA embeds itself into the baby’s DNA causing mutations. Gene therapy using homologous recombination of small fragments has shown that amounts as small as 1.9 ng / mL of DNA fragments result in genome insertion of stem cells in 100% of injected mice. Levels of human fetal DNA fragments in our children after vaccination with MMR, VARIVAX (varicella) or hepatitis A vaccines reach levels above 1.9 ng / mL.
- autoimmune disease: fetal human DNA stimulates the immune system’s reaction to attack the body of the boy / girl.
Our results greatly reinforce the experimental observations of Dr. Deisher and above all the fact that the contaminating fetal DNA present in all the samples analyzed in variable (therefore uncontrolled) quantities is up to 300 times higher than the limit imposed by the EMA for Carcinogenic DNA (10 ng / dose, corresponding to the DNA contained in about 1000 cancer cells, obtained on the basis of a statistical calculation, while the precautionary limit is 100 pg / dose) limit that must necessarily also be applied to fetal DNA which inevitably contaminates the Priorix Tetra.
It follows that this vaccine must be considered defective and potentially dangerous for human health, in particular of the pediatric population much more vulnerable to genetic and autoimmune damage due to immaturity in shelter systems.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7059852/
- https://www.corvelva.it/speciale-corvelva/vaccinegate/analysis-metagenomiche-su-priorix-tetra.html
- https://www.corvelva.it/speciale-corvelva/vaccinegate.html
https://www.corvelva.it/speciale-corvelva/vaccinegate-en.html - https://www.corvelva.it/speciale-corvelva/vaccinegate/sequenziamento-del-genoma-completo-di-mrc-5-contenuto-in-priorix-tetra.html
- https://www.corvelva.it/speciale-corvelva/vaccinegate/analysis-metagenomiche-su-priorix-tetra.html
- https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2010/03/04/2010-4553/guidance-for-industry-characterization-and-qualification-of-cell-substrates-and-other-biological
- https://www.who.int/biologicals/vaccines/TRS_978_Annex_3.pdf
- https://www.corvelva.it/speciale-corvelva/vaccinegate/sequenziamento-del-genoma-completo-di-mrc-5-contenuto-in-priorix-tetra.html
- https://www.corvelva.it/approfondimenti/notizie/mondo/lettera-aperta-ai-legislatori-sul-dna-fetale-nei-vaccini-theresa-deisher.html